Difference between revisions of "Computational Theories of Mindfulness"
(→Psychological Mechanisms) |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Evidence for mindfulness practice improving sustained attention and attentional control processes exists. Enhanced cognitive control network activity is associated with increased psychological well-being [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29628063/] [https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0219862] [https://link.springer.com/article/10.3758/s13428-019-01308-z]. | Evidence for mindfulness practice improving sustained attention and attentional control processes exists. Enhanced cognitive control network activity is associated with increased psychological well-being [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29628063/] [https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0219862] [https://link.springer.com/article/10.3758/s13428-019-01308-z]. | ||
| − | '''Therapies | + | '''Therapies''' |
| − | ''' | + | |
| − | Mindfulness offers a framework of self-awareness, -regulation, and -transcendence that can be implemented in psychological intervention methods | + | Mindfulness offers a framework of self-awareness, -regulation, and -transcendence that can be implemented in psychological intervention methods [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3480633/]. Mindfulness is now incorporated as a major component of empirically supported psychological intervention methods, including [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mindfulness-based_stress_reduction mindfulness-based stress reduction] (MSBR) [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0163834382900263?via%3Dihub], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mindfulness-based_cognitive_therapy mindfulness-based cognitive therapy] (MBCT) [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221413911930099X#:~:text=Study%20shows%20that%20MBCT%20has,depressive%20symptoms%20than%20psycho%2Deducation.&text=MBCT%20significantly%20decrease%20depression%20severity,response%20rate%20but%20not%20remission.&text=MBCT%20shows%20significant%20decrease%20in%20depressive%20symptoms%20and%20improve%20the%20mindfulness%20skill], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acceptance_and_commitment_therapy acceptance and commitment therapy], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dialectical_behavior_therapy dialectical behavior therapy] [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12671-017-0742-x#ref-CR60]. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Neurophysiological mechanisms == | ||
Revision as of 23:45, 21 October 2022
By Liza Tatishev
Mindfulness involves non-judgmental moment-to-moment self-awareness of physical and mental states– it is the ability to be fully conscious and aware. Within the past decade, scientific interest in mindfulness practices has increased. Mindfulness has a long history: originating over 2,500 years ago in Indian Buddhist tradition [1]. By the mid-twentieth century, mindfulness became secularized and incorporated into psychological intervention methods to improve emotional well-being [2]. Today, mindfulness-based intervention methods are recognized as successful approaches in treating a variety of psychological disorders, including depression, anxiety, and addiction. A more precise understanding of mindfulness can benefit the refinement of mindfulness-based intervention methods.
A more precise understanding of mindfulness can benefit the refinement of mindfulness-based intervention methods. Artificial neural networks within the field of computational neuroscience offer a method to examine the neuroscience of mindfulness.
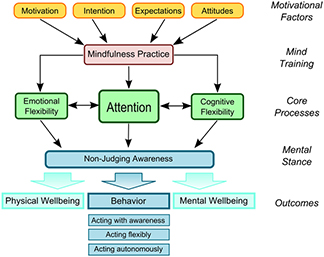
Psychological Mechanisms
As a psychological intervention method, mindfulness practices– such as Tibetan Buddhist imagery meditation [3], Zen meditation [4], and Kundalini yoga [5]– are grounded in training and refining attention skills. Attentional control is a key cognitive process of executive functioning (also referred to as cognitive control) necessary for emotional and behavioral regulation [6].
Cognitive control
Mindfulness training has been shown to enhance cognitive control in children and adults [7]. On a phenomenological level, the process of mindfulness training engages with the self-regulation of cognitive states that are interrelated with attentional networks.
Within cognitive psychology, attention consists of sub-processes (including alerting, sustained attention, and conflict monitoring) that underlie the ability to attend to stimuli. Higher self-reported mindfulness is related to higher measures of more stable sustained attention [9]. Furthermore, longitudinal studies have found that engaging in mindfulness practices correlated with improvement in sustained attention tasks over the course of intervention [10].
Sustained attention recruits attentional control functions, while inhibiting proponent, but non-relevant responses [11]. Research has demonstrated that mindfulness may improve performance on attentional control tasks, however experimental designs should be improved to remove discrepancies in the field [12].
Evidence for mindfulness practice improving sustained attention and attentional control processes exists. Enhanced cognitive control network activity is associated with increased psychological well-being [13] [14] [15].
Therapies
Mindfulness offers a framework of self-awareness, -regulation, and -transcendence that can be implemented in psychological intervention methods [16]. Mindfulness is now incorporated as a major component of empirically supported psychological intervention methods, including mindfulness-based stress reduction (MSBR) [17], mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) [18], acceptance and commitment therapy, and dialectical behavior therapy [19].